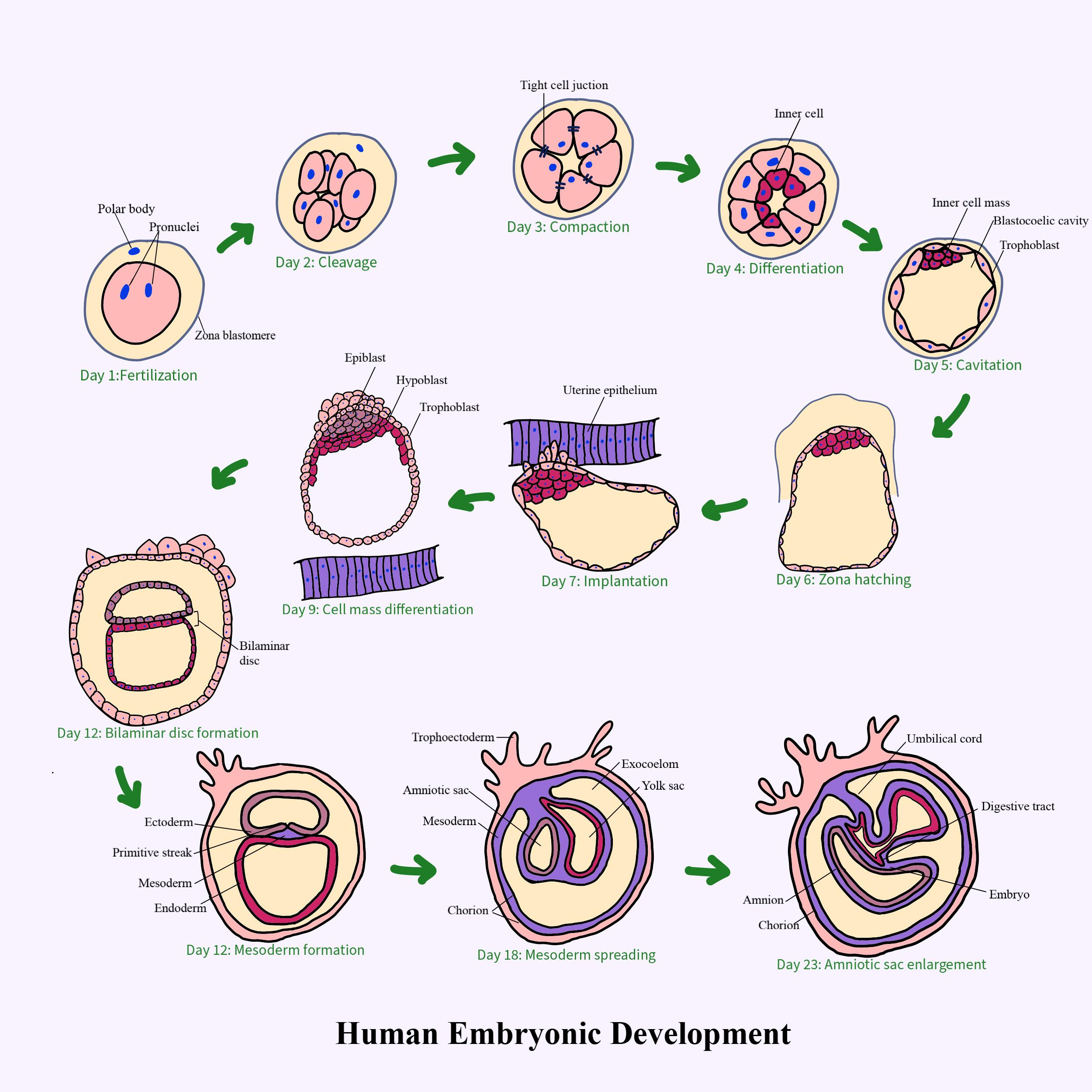
New approaches to embryo selection Biology Diagrams Accordingly, the embryonic cell cycle exhibits a high degree of plasticity; however, the mechanisms underlying its regulation in vivo remain largely unknown. The purpose of this review is to summarize the data on cell cycle regulation during the early mouse embryonic development, a period characterized by major variations in cell cycle In many species, early development initiates with rapid and almost synchronous mitotic divisions that slow over time as the embryo approaches the key developmental transition to gastrulation (Foe et al., 1993; O'Farrell, 2015).These early divisions are much faster than somatic divisions in adult tissues and do not contain gap phases of the cell cycle (Farrell and O'Farrell, 2014); the cell
Early embryonic development is characterized by a plethora of very complex and simultaneously operating processes, which are constantly changing cellular morphology and behaviour. Regulation of the cell cycle in early mammalian embryos and its clinical implications Int J Dev Biol. 2019;63(3-4-5):113-122. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.180400ma.
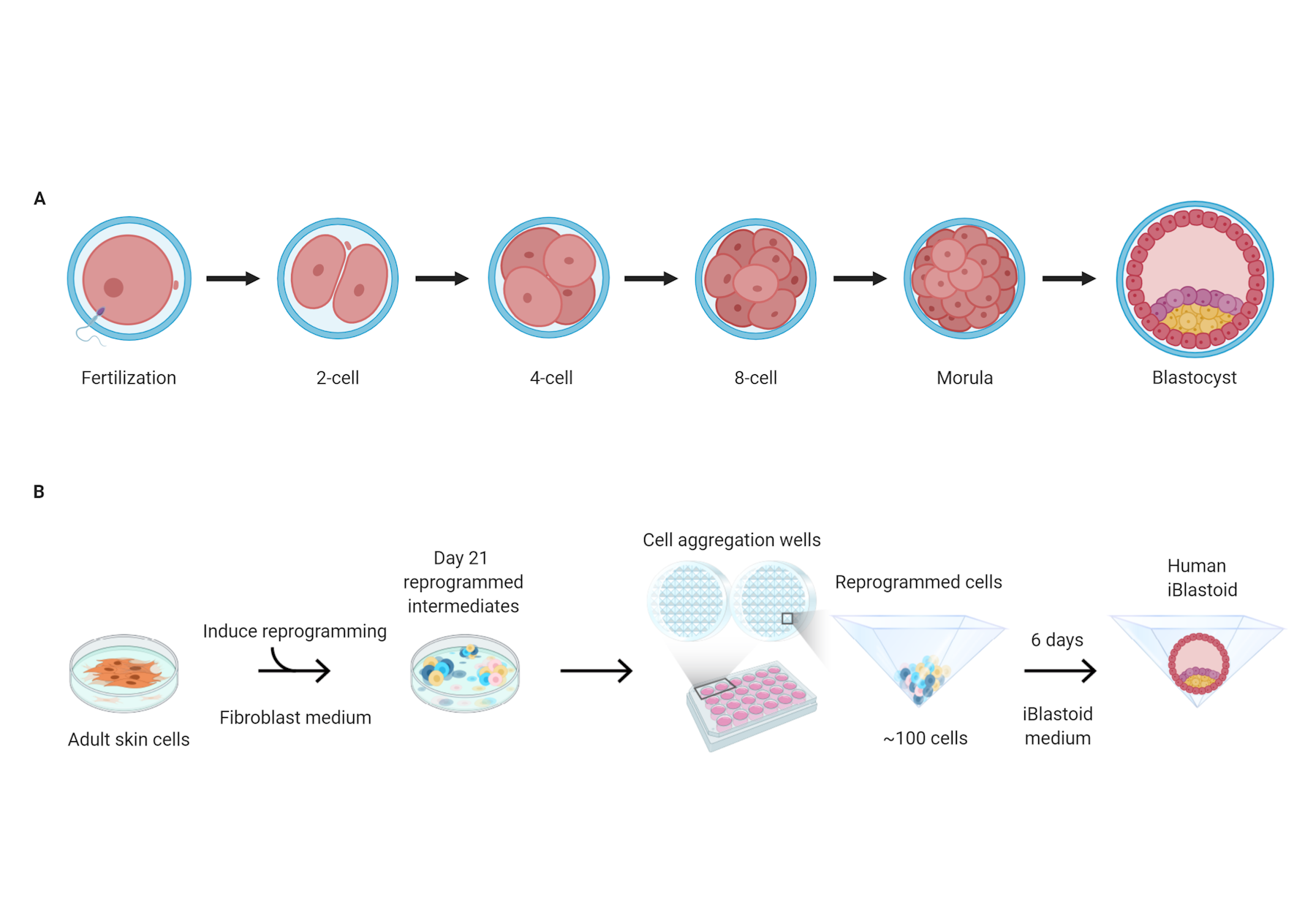
Cell cycle regulation during early mouse embryogenesis Biology Diagrams
Understanding the mechanisms of embryonic cell cycles is a central goal of developmental biology, as the regulation of the cell cycle must be closely coordinated with other events during early embryogenesis. Quantitative imaging approaches have recently begun to reveal how the cell cycle oscillator …

The synthesis and destruction of cyclin B drives mitosis in eukaryotic cells. Cell cycle progression is also regulated at the level of cyclin B translation. In cycling extracts from Xenopus embryos, progression into M phase requires the polyadenylation-induced translation of cyclin B1 mRNA. Polyadenylation is mediated by the phosphorylation of CPEB by Aurora, a kinase whose activity oscillates

Molecular ties between the cell cycle and differentiation in embryonic ... Biology Diagrams
Embryonic cells sense temporal gradients of regulatory signals to determine whether and when to proceed or remodel the cell cycle. Such a control mechanism is allowed to accurately link the cell cycle with the developmental program, including cell differentiation, morphogenesis, and gene expression.